Building your Threat Intelligence dream team
Fujitsu / February 12, 2025
As cyber security threats grow more sophisticated, organizations increasingly rely on Threat Intelligence (TI) to anticipate, identify, and mitigate risks. This guide explores the essential elements, methodologies, and best practices for building an effective TI capability.
What is Threat Intelligence?
TI involves collecting, analyzing, and applying information about cyber threats to enhance security. It enables organizations to anticipate risks, improve decision-making, strengthen incident response, support compliance, safeguard reputation, and gain a competitive edge.
An effective TI capability follows a structured methodology approach.
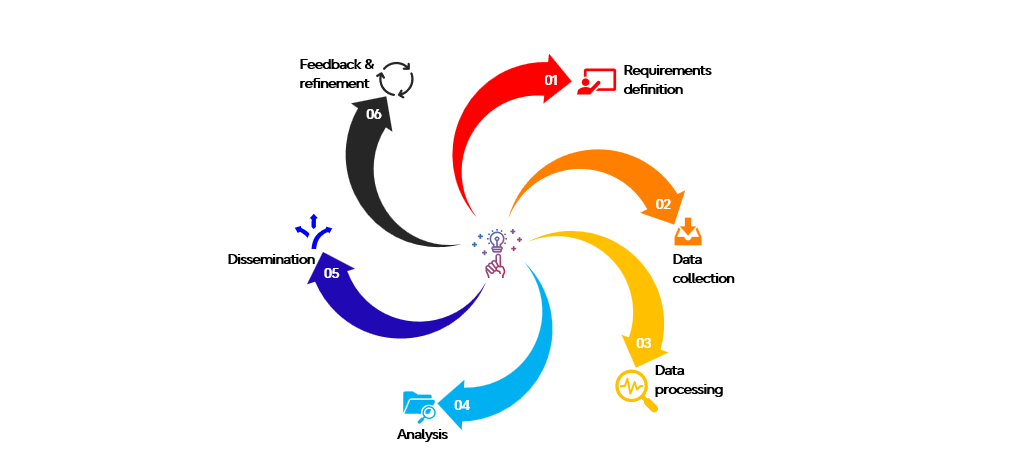
1. Requirements definition: Identifying the intelligence needs and objectives of the organisation.
2. Data collection: Gathering relevant threat data from a variety of internal and external sources.
3. Data processing: Cleaning, normalising, and enriching the raw data to make it usable for analysis.
4. Analysis: Identifying patterns, trends, and actionable insights from the processed data.
5. Dissemination: Sharing the insights with relevant stakeholders in an understandable and actionable format and with security tools such as Firewalls, IDS*, SIEM, SOAR, Endpoints as examples.
6. Feedback and refinement: Continuously refining the Threat Intelligence process based on stakeholder feedback and evolving requirements.
Categories of Threat Intelligence
Businesses may consume one or more of the listed TI forms based on its purpose and scope.
• Strategic TI: High-level insights for long-term decision-making, ideal for executives and risk managers. While non-technical, Intel looks further ahead, focusing on long-term risks, emerging adversaries, geopolitical factors as examples. Sources include OSINT, ISACs*, NGOs and media news publications alongside whitepapers and research reports.
• Operational TI: Immediate threat information to support incident response and threat hunting activities. Sources include dark web and forums, malware analysis, security feeds/alerts and social media platforms.
• Tactical TI: Attack patterns and methods to strengthen defenses. Sources include cyber security community forums, threat databases, Dark Ops and public attack surface monitoring.
• Technical TI: Short-term indicators of compromise, such as malicious IPs and domains. Sources include threat data feeds, research reports, communities, hacker forums and learnings from an attacked organization.
A guide to Threat Intelligence capability
Robust TI capability comprises of the following key components: people, process and technology. While processes and technology are critical for efficiency and scalability, it is the expertise and judgment of human analysts that bring clarity and actionable value to TI efforts.
Therefore, we have three recommendations for you:
1. Aligning team structure with business needs
A robust TI capability requires a well-defined team structure. Match the intelligence capability with organizational objectives. Effective TI relies on a team with clear roles, responsibilities, and required skills, and ensuring the team structure supports both strategic and operational needs.
2. Focus on business relevance and effectiveness
Strong communication channels between TI teams and other business units are critical for maintaining relevance and ensuring actionable insights. Identify critical success factors, and how they will be managed, as part of service design activities. An example of this would be to consider/review dissemination phase of the TI process and identify various integration points. Create collaborative forums or peering matrices to align TI with business needs and implement continuous feedback loops to refine intelligence processes.
3. Consider outsourcing scope and automation
Outsourcing TI capabilities can fill skill gaps, but clarity in business requirements and team structures is essential. Consider including automation of processes that are mature (defined, repeatable and measurable) within the contract. The aim is to calibrate the accuracy and relevance of incoming information and data that is processed via automation. Make sure partners understand your organization’s needs and risks.
Conclusion
A strong TI capability relies on skilled analysts, robust processes, and advanced technology to deliver actionable cyber security insights. By aligning team structures, defining clear roles, levering the power of automation, and setting external sharing policies, organizations can effectively anticipate and mitigate cyber threats. Regularly measure performance and refine processes to ensure sustained success.
With TI capability playing a pivotal role in your overall cyber security strategy, it is paramount to approach it in a measured way. Fujitsu hopes to partner with you along this journey as you enhance your cyber security posture. Get in touch with your Fujitsu sales rep for a detailed discussion on this topic.
* Abbreviations: IDS = Intrusion Detection System, SIEM = Security Information and Event Management, SOAR = Security Orchestration, Automation and Response, CISO = Chief Information Security Officer, OSINT = Open Source Intelligence, ISAC = Information Sharing and Analysis Center, NGO = Non Governmental Organization, Dark Ops = Dark Operations, IPs = Internet Protocol addresses.

Vijay Chakravarthy | LinkedIn
Editor's Picks












