Sustainable AI – Transforming Agriculture
Fujitsu / January 7, 2025
The growing application of AI in agriculture offers a transformative opportunity to address some of the world's most pressing challenges. By optimizing resource use, increasing crop yields, and minimizing waste, AI is not only revolutionizing agriculture, but also contributing to a more sustainable future. The development of Sustainable AI has the potential to take it to the next level, allowing us to meet the demands of a growing global population without compromising the health of our planet.
Contents
- The Challenge of Sustainable Agriculture
- Sustainable AI in Agricultural Research
- Precision Agriculture: Optimizing Resource Utilization
- AI-Driven Robotics in Agriculture
- Optimizing Agricultural Supply Chains
- Smart Agriculture: Greenhouse and Vertical Farming
- Urban and Vertical Farming: The Future of Agriculture
- Mitigating the Environmental Impact of Greenhouse Farming
- The future of Farming
- Conclusion
The Challenge of Sustainable Agriculture
Feeding a growing global population while minimizing environmental impact is one of the most pressing challenges of our time. Agriculture, a cornerstone of human survival, is paradoxically a major contributor to CO2 emissions. The rising living standards in many parts of the world exacerbate this issue, as dietary shifts increase per capita carbon footprints. Compounding these challenges is the fact that many countries have surpassed their domestic food production capacities, relying heavily on global food supply chains another significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. In this context, the question arises: How can we produce more food sustainably?
Emerging technologies, particularly Artificial Intelligence (AI), offer transformative solutions. From improving crop yields to optimizing supply chains, AI is paving the way for a more sustainable agricultural future. Fujitsu and other innovative firms are spearheading efforts to apply AI in precision agriculture, greenhouse farming, and supply chain optimization, ensuring that sustainability and productivity go hand in hand.
Our whitepaper “Sustainable AI for Enterprise Transformation, Innovation and Growth”, provides an overview of how such initiatives can now be integrated with the support of Sustainable AI platforms that can further drive sustainable change in agriculture. This blog post summarizes some of the most important applications.
Sustainable AI in Agricultural Research
AI's growing role in agricultural research is revolutionizing how we develop crops with higher yields and greater resilience to climate change. Bayer's Climate FieldView platform, for instance, uses AI to analyze data from various sources, helping researchers create drought-tolerant and disease-resistant crops. Similarly, Corteva Agriscience's Granular software leverages AI to offer insights into soil health and crop performance, enabling the adoption of more sustainable farming practices.
Genomics research—a cornerstone of future agriculture—relies heavily on AI-based data analysis and predictive modeling. Transparent and ethical implementation of Sustainable AI ensures that these advancements are both impactful and equitable. Fujitsu’s computational platforms have shown promise in processing massive datasets for agricultural genomics, accelerating the discovery of climate-resilient crop traits.
For instance, by using AI-driven genomics analysis, researchers can identify beneficial traits in crops at a fraction of the time it traditionally takes. This accelerates the development of drought-resistant crops, which are critical in regions facing water scarcity. The ability to predict how crops will perform under various climatic conditions allows researchers to design strategies that mitigate risks posed by climate change.
Precision Agriculture: Optimizing Resource Utilization
Precision agriculture employs AI to map fields, monitor crops, and manage resources with unparalleled accuracy. By enabling farmers to apply fertilizers, pesticides, and water only where needed, it reduces environmental impact while maximizing yields. For example, John Deere's See & Spray technology uses computer vision and machine learning to identify weeds and apply herbicides only to affected areas, reducing chemical use by up to 90%. IBM's Watson Decision Platform for Agriculture integrates AI-driven insights on weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop health, empowering farmers to make informed decisions.
Early on, Fujitsu had developed the Akisai Food and Agricultural Cloud, which employs advanced AI algorithms to monitor environmental conditions and optimize crop management. This technology has demonstrated significant reductions in water and chemical usage, setting a benchmark for sustainable farming.
The benefits of precision agriculture extend beyond resource optimization. By integrating AI-powered sensors and drones, farmers can gain real-time data on crop health, soil quality, and pest infestations. This data allows for targeted interventions, reducing wastage and ensuring healthier crops. Precision agriculture is not only a tool for large-scale commercial farms but also an enabler for smallholder farmers, equipping them with insights to improve their productivity and livelihoods.
AI-Driven Robotics in Agriculture
Robotic agriculture is another frontier where AI is making a significant impact. Robots equipped with machine learning and computer vision are increasingly being deployed for tasks such as weeding and harvesting. Bosch’s Bonirob, for example, identifies and removes weeds mechanically, eliminating the need for chemical herbicides. Although developed over a decade ago, such technologies are being refined and enhanced through Sustainable AI to deliver even greater efficiencies.
Fujitsu’s robotics research is also contributing to this field, with prototypes designed to work seamlessly across various crop types and field conditions. These robots not only reduce labor costs but also help minimize resource wastage, contributing to the broader goals of precision agriculture.
Additionally, robotic harvesters are being equipped with advanced AI to identify and pick ripe fruits and vegetables without damaging the produce. Such innovations are addressing labor shortages in agriculture while ensuring that harvesting is conducted efficiently and sustainably. The integration of Sustainable AI ensures that these systems operate with minimal environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Optimizing Agricultural Supply Chains
AI plays a pivotal role in streamlining agricultural supply chains, reducing wastage, and minimizing the carbon footprint of food production. AI-powered image recognition systems are now widely used to sort, grade, and package produce with unprecedented accuracy. For instance, TOMRA Sorting Solutions employs machine learning to ensure only high-quality fruits and vegetables reach consumers, significantly reducing food waste.
Startups like AgShift are leveraging AI to automate quality assessments, minimizing human error, and enhancing supply chain efficiency. Fujitsu’s "Farm to Fork" initiative exemplifies how AI-based analytics can integrate supply chain quality management (SCQM), improving food safety and reducing risks. These advancements ensure that agricultural supply chains are not only efficient but also sustainable.
AI-driven logistics platforms also play a role in minimizing transportation emissions by optimizing delivery routes and schedules. This ensures that perishable goods reach their destination faster, reducing spoilage and waste. Additionally, predictive analytics helps suppliers anticipate demand, preventing overproduction and the associated environmental costs.
Smart Agriculture: Greenhouse and Vertical Farming
Greenhouse farming, a cornerstone of smart agriculture, addresses the challenges of traditional farming by offering controlled environments for crop cultivation. It is growing at a fast pace in most regions, not only in the North with adverse weather conditions, but increasingly in the South - mainly due to water shortages - as well.
Smart Agriculture Market Size (Bn USD, 2018-30 Growth)
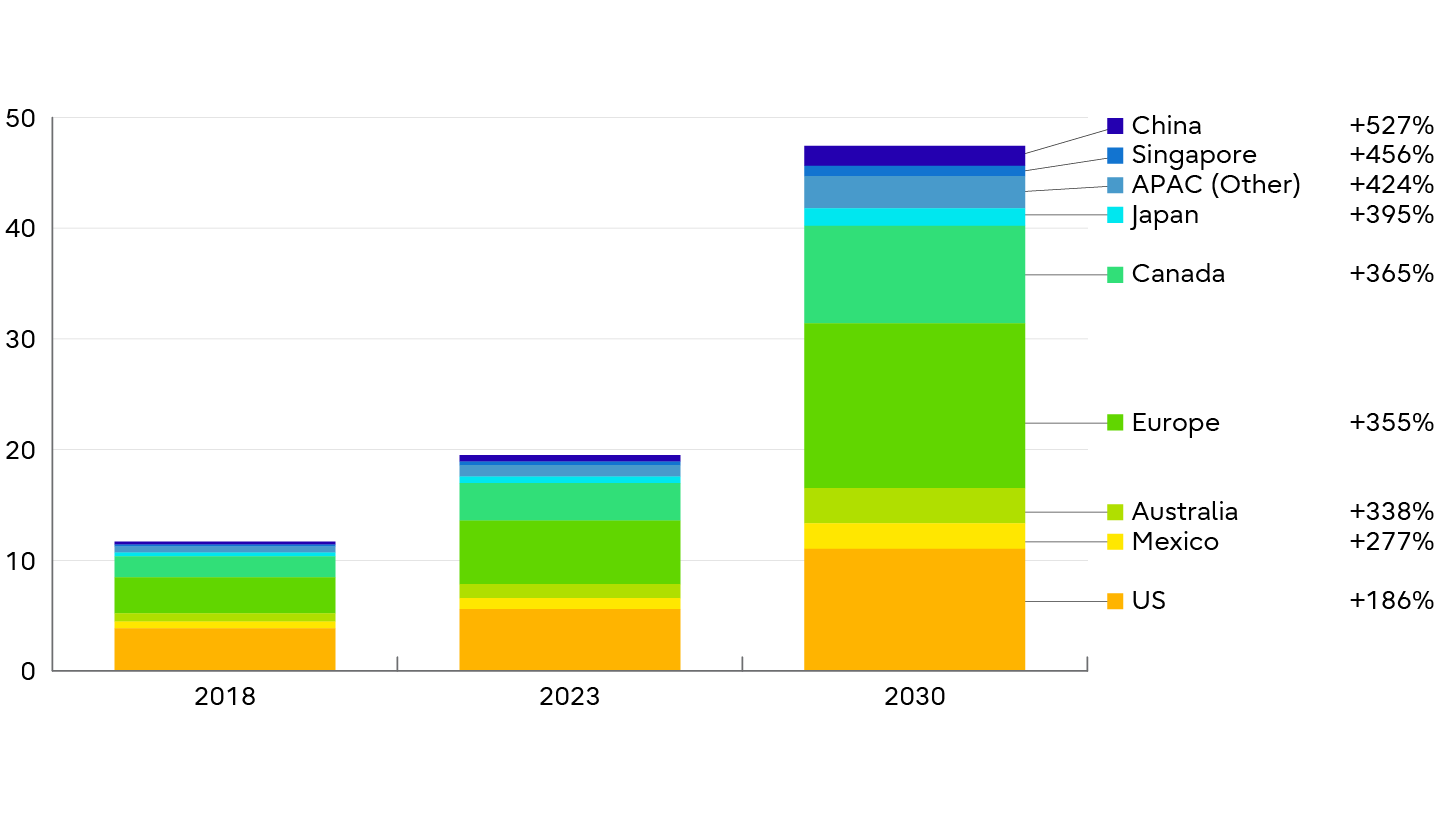
Source: Grand View Research (2024) - Smart Agriculture Market.
However, the energy demands of greenhouses—for heating, cooling, and lighting—pose significant sustainability challenges. In Canada, for example, greenhouse energy consumption has increased by 55% over the past decade despite doubling produce output.
Fujitsu’s Akisai platform has demonstrated how AI can optimize greenhouse operations. By monitoring humidity, temperature, and CO2 levels, the platform provides real-time insights that help reduce energy consumption while maximizing yields. Fujitsu’s partnership with Botanical Water Technologies exemplifies innovative approaches to water conservation, such as extracting usable water from greenhouse humidity.
In addition to energy efficiency, AI can optimize the selection of crops best suited for greenhouse farming. By analyzing market trends, weather forecasts, and resource availability, AI platforms can recommend crop rotations that maximize profitability and sustainability. The integration of renewable energy solutions, such as solar-powered greenhouses, further enhances the environmental benefits of this approach.
Urban and Vertical Farming: The Future of Agriculture
Vertical farming, an advanced form of Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA), represents the future of urban food production. By growing crops in stacked layers within urban settings, vertical farming minimizes land use and transportation emissions. Fujitsu’s has experimented with using semiconductor clean rooms for lettuce production illustrate the potential of this approach. The bacteria-free environment eliminates the need for pesticides and reduces cooling requirements during delivery.
Vertical Future, a Fujitsu partner, has developed automated vertical farms that use up to 98% less water than traditional farming methods. These farms are powered by AI algorithms that optimize light, temperature, and nutrient levels, ensuring sustainable and high-yield production. As urban populations grow, vertical farming offers a scalable solution to food security.
The scalability of vertical farming extends to diverse crops, including leafy greens, berries, and herbs. With the support of AI, these systems can be adapted to different urban settings, from repurposed industrial spaces to purpose-built facilities. The technology also opens doors for hyper-local food production, reducing reliance on long-distance transportation and ensuring fresher produce for consumers.
Mitigating the Environmental Impact of Greenhouse Farming
While greenhouse and vertical farming offer significant advantages, their energy consumption remains a critical concern. AI can help mitigate these challenges by optimizing resource use and integrating renewable energy solutions. For instance, solar startups are developing transparent and UV-absorbing solar glass that can generate energy while maintaining optimal light conditions for plants.
In Europe, the EU-sponsored The Greefa project is exploring innovative approaches such as using salt solutions to convert greenhouse humidity into heat, reducing thermal energy demand by 50%. Fujitsu’s research into integrating AI with renewable energy systems further underscores the potential of Sustainable AI in minimizing the carbon footprint of smart agriculture.
The Future of Farming
As agriculture evolves, the integration of AI into farming practices will play a pivotal role in addressing global food security challenges. From precision agriculture to vertical farming, AI enables farmers to produce more food with fewer resources, reducing the environmental impact of food production.
Fujitsu’s commitment to Sustainable AI ensures that these advancements are both ethical and effective. By leveraging its expertise in AI, robotics, and supply chain management, Fujitsu is helping to create a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand. The journey from farm to fork is being redefined, and with the right innovations, the agricultural sector can become a model of sustainable development.
Conclusion
The convergence of AI and agriculture offers a transformative opportunity to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges. By optimizing resource use, enhancing crop yields, and minimizing waste, AI is not only revolutionizing agriculture but also contributing to a more sustainable future. Fujitsu’s pioneering efforts in this space highlight the potential of technology to drive positive change, ensuring that agriculture can meet the demands of a growing global population without compromising the planet’s health.
So, why not talk to Fujitsu and find out how we can help you harness the power of Sustainable AI? You can also find out more about the transformative potential of Sustainable AI in our white paper “Sustainable AI for Enterprise Transformation, Innovation and Growth.”

Today, Nick is a Principal Consultant & Fujitsu Distinguished Engineer within the Fujitsu Global Technology Strategy Unit.
Nick Cowell nick.cowell@fujitsu.com



