Sustainable AI – Leading Industry into the Intelligent Age
Fujitsu / January 14, 2025
Sustainable AI is becoming an indispensable technology for implementing sustainable business models. In industry, it can build on the strongest base of smart technologies already promoted by initiatives such as Industry 4.0 or the World Economic Forum's current push for an Intelligent Age. The article shows how Sustainable AI systems can support the journey towards sustainable manufacturing.
Contents
- Sustainable AI in Industry
- From Industry 4.0 to Sustainable Technologies
- Reality Check - Industry 4.0 has Failed the Environment
- Advanced ‘Global Lighthouse’ Companies Now Paving the Way
- Generative AI as an Enabler of Business Transformation
- Steps towards a Circular Economy
- Automotive Industry Leads the Way
- Conclusion
Sustainable AI in Industry
In our Whitepaper “Sustainable AI for Enterprise Transformation, Innovation and Growth”, we show how the development and implementation of Sustainable AI platforms can become a driving force for enterprise transformation and fostering sustainable growth. It shows how AI, especially generative AI, can integrate with existing management systems to improve prediction, optimization, and planning across multiple business functions. It enables data-driven decision-making and streamlines complex sustainability initiatives across departments and value chains.
Sustainable AI Platform
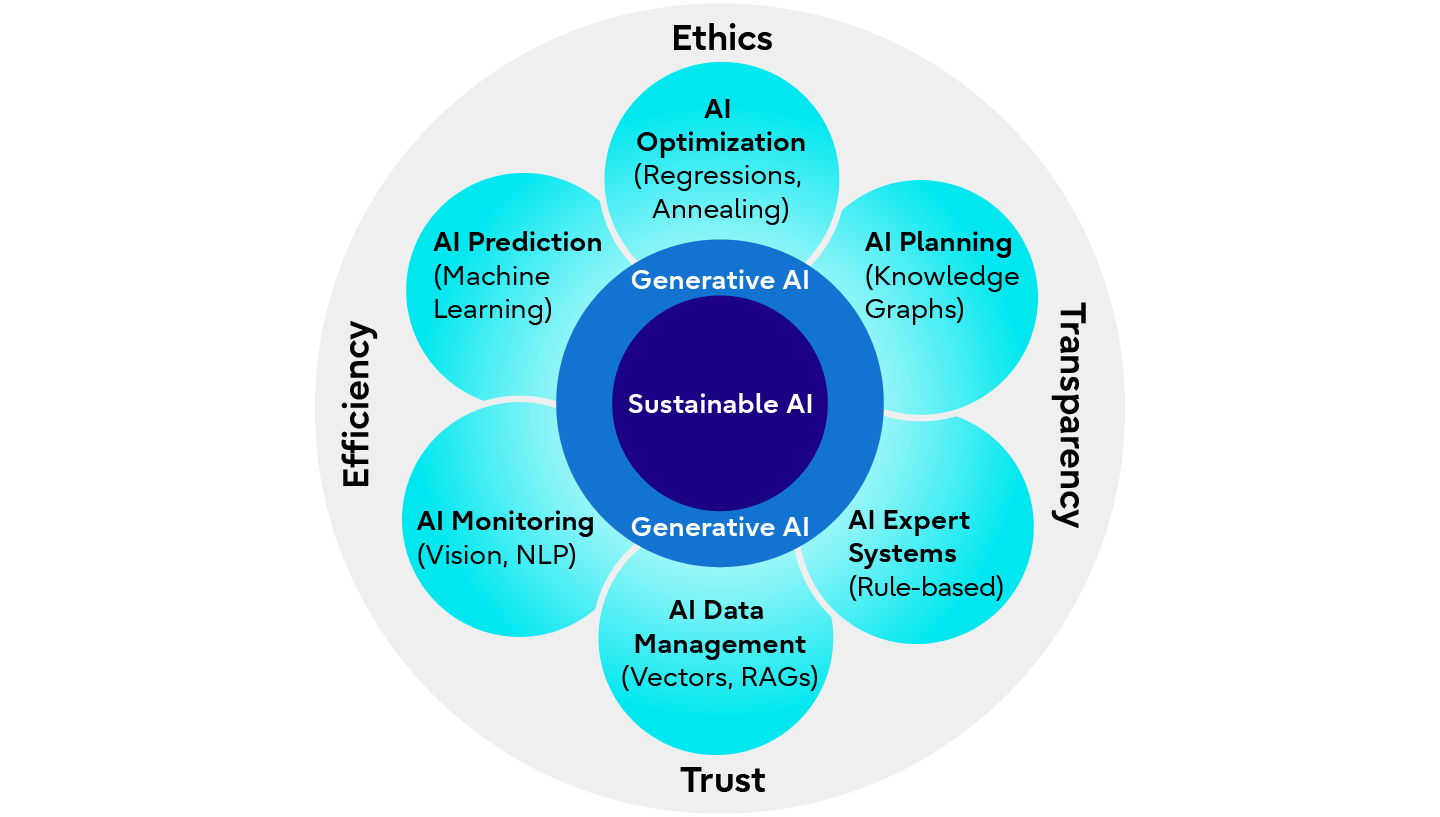
Source: https://activate.fujitsu/en/key-technologies-article/ta-sustainable-ai-20241129
Aligning AI technologies with sustainability goals can be empowering and beneficial on many levels. Implementation based on a Generative AI platform core enables seamless access and integration of existing information silos, unstructured corporate documents, and human communications. As more data and information flows become available, Generative AI platforms can help integrate existing management systems for forecasting, optimization, and planning for sustainable solutions.
Generative AI can also help deliver this information to management in the language and level of detail they need to quickly develop actionable solutions. Without such platform integration, management would remain blind to the potential of most sustainability opportunities.
From Industry 4.0 to Sustainable Technologies
More than a decade ago, the Industry 4.0 initiative helped to connect a growing number of sensors and devices (the Internet of Things or IoT) with cloud computing, big data analytics, AI control, and advanced robotics.
In Japan, the potential was quickly recognized and expanded into a much broader, service-oriented, and socially inclusive Society 5.0 model. In the rapidly ageing country, it was seen as helping not only to modernize industry, but also to future-proof the entire economy, which had been challenged by slowing growth, resistance to change and loss of technology leadership.
More recently in Europe, the Industry 5.0 initiative has added sustainability, resilience, and a more human-centered perspective to the ongoing Digital Transformation (DX) of industry.
Last year, the World Economic Forum (WEF) further developed its concept of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, with AI at its core, and chose Collaboration for the Intelligent Age as the theme for its 2025 annual meeting in Davos to discuss its future potential. It hopes to garner support for the development of international frameworks that balance environmental, social, and geopolitical intelligence with technological intelligence.
Reality Check - Industry 4.0 has Failed the Environment
However, the resulting productivity gains from digital transformation have not yet translated into significant improvements in environmental sustainability. Even a significant reduction in industrial greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, which has been the focus of environmental policy for the past decade, has not yet been achieved.
As the chart for GHG emissions in Germany shows, even this environmentally conscious country, with its large and highly productive manufacturing sector, has not managed to reduce industrial emissions since the start of the Industry 4.0 initiative in 2011.
In contrast to the energy sector, which is benefiting from the introduction of renewable energy technologies, industrial emissions stagnated at a high level. As less efficient and higher-emitting production moved to emerging economies, global industrial emissions continued to rise. The only major decline in 2023 is triggered by the negative shock of rising energy costs since the war in Ukraine.
GHG Emissions in Germany (2010=100)
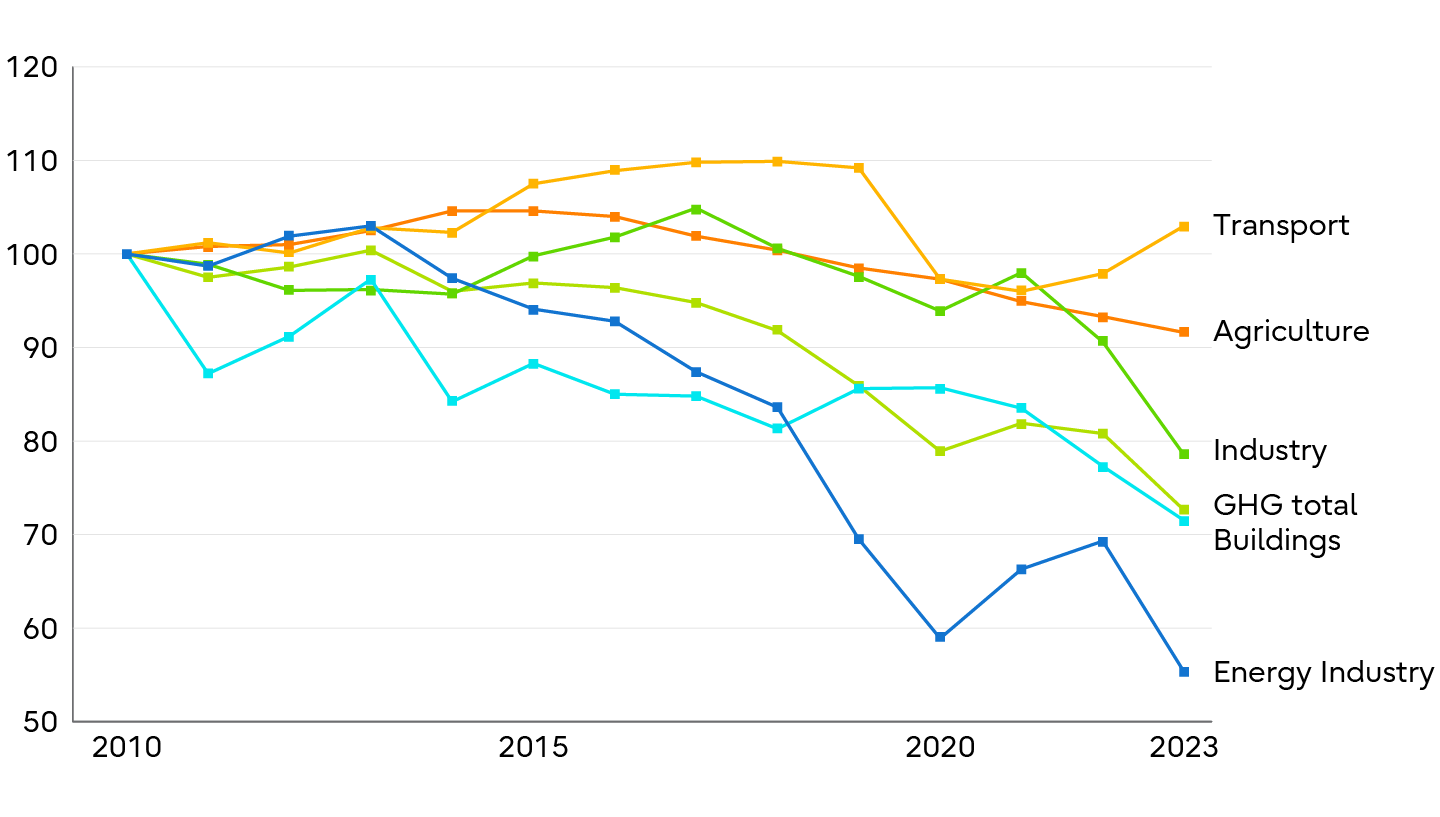
Source: Bundesumweltamt (2024).
Advanced ‘Global Lighthouse’ Companies Now Paving the Way
An increased focus on sustainability and rapidly advancing AI technologies now offer new hope that economic and environmental gains can be better aligned. Our blog post on Double Materiality explained how AI can be used to address these seemingly divergent goals simultaneously. In particular, Generative AI platforms can help integrate existing management systems for forecasting, optimization, and planning with sustainable solutions.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) and McKinsey argue that the implementation of Industry 4.0 has not led to the expected benefits across industries because it requires the transformation of entire organizations, which is time-consuming and requires strong role models.
Their Global Lighthouse Network of advanced manufacturing companies is designed to support such transformation by demonstrating strong productivity gains and developing role models.
Since its inception in 2019, this group of advanced companies has been able to increase its productivity by 15-30%. Each cohort of companies added to the network so far has increasingly focused on AI as the conductor of their technology development. The most recent cohort of Lighthouse companies (December 2023) achieved AI-related productivity improvements of 10-20% in their supply chain operations, over 40% in process optimization, and over 30% in assembly, quality, and testing.
In 2021, the WEF Lighthouse Project added a new category of "Sustainability Lighthouse" leaders to further explore environmental potential. But even among these advanced companies, progress has been slow. Of the 103 Lighthouse companies, about 60% were working on sustainability-related projects, but only 6 were recognized as Sustainability Leaders in 2022.
Generative AI as an Enabler of Business Transformation
The introduction of Generative AI can now provide an additional boost. In our whitepaper “Generative AI Innovation – Where is the Business Value,” we have shown that Generative AI can indeed deliver significant improvements across all business functions. As companies realize the power of Generative AI platforms for flexible information integration, human-machine communication, and work integration, they have begun to gradually transform more and more business functions, enabling better integration of sustainable goals and environmental benefits.
The figure below provides an overview of the link between AI technologies and the business functions being transformed by Generative AI platforms. All major functions, from data management to R&D and learning, show great potential for AI-based productivity gains. Given the potential of Sustainable AI, the "materiality" of sustainable and environmental requirements could now be embedded in all of these functions simultaneously, taking the modernization of Industry 4.0 systems a big step toward sustainable manufacturing.
Generative AI Integration of Technology and Business Functions
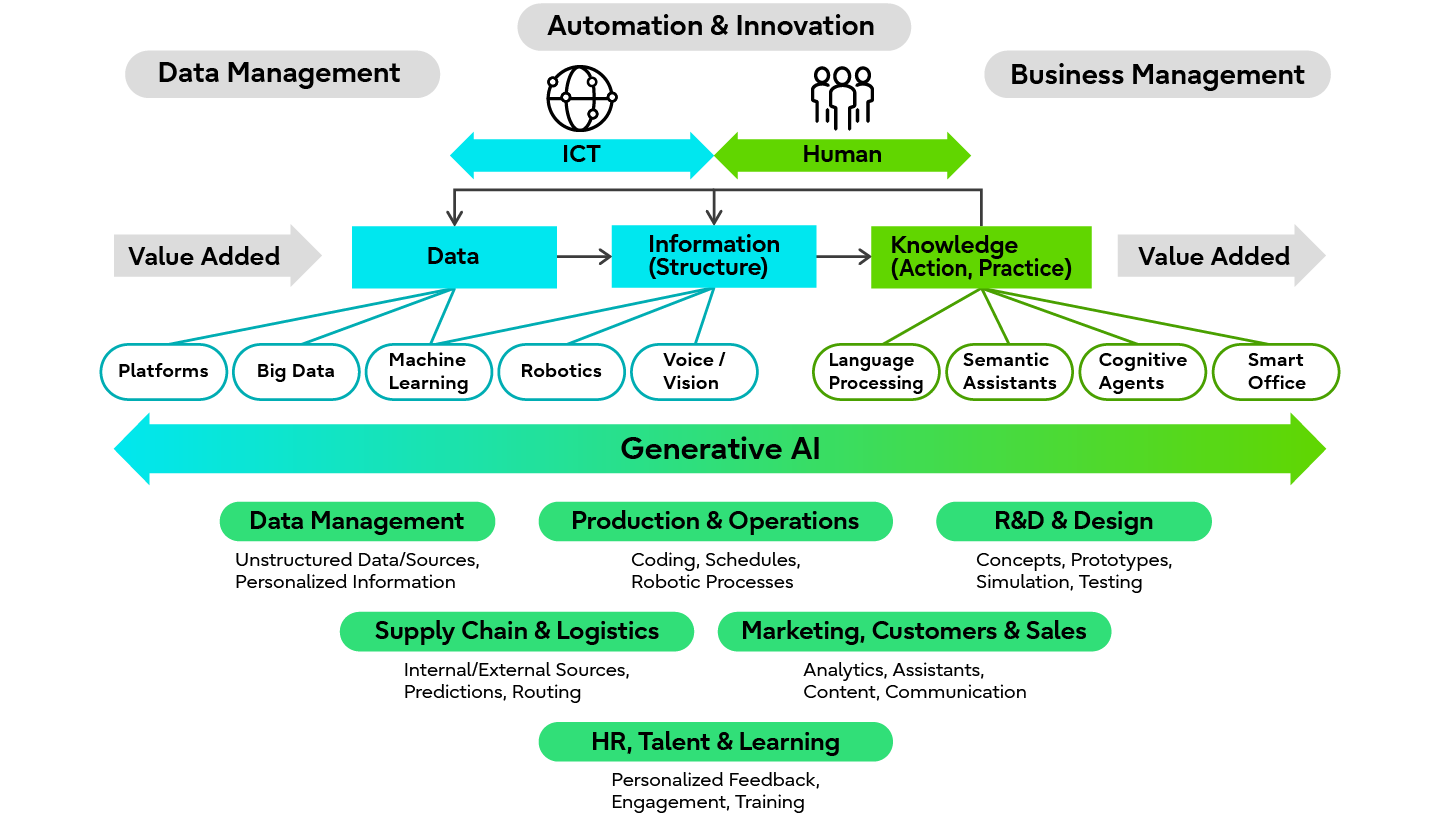
Steps towards a Circular Economy
While Generative AI opens up new opportunities to integrate sustainability goals into business functions, it is likely that regulatory requirements, rather than technological opportunities, will continue to drive major changes in the industry. Although regulatory enthusiasm for meeting climate targets has waned and industry has backed away from targets that are unlikely to be met, existing regulations are having an increasing impact and most companies are sticking to their environmental goals.
Starting this year, carbon reduction requirements and carbon pricing will demand significant reductions in carbon footprints. Sitting at the center of long supply chains for the manufacture of products with often high carbon footprints, industry needs to assess the entire carbon economy to improve the sustainability of their operations and products.
The result is an innovative approach to managing data across the entire value chain, from material certification to digital twin-based design for lifecycle improvement and disposal orchestration. This requires Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and blockchains, to monitor increasingly circular processes, and Sustainable AI to manage them.
Industry 4.0 and Circular Economy Data and Technologies
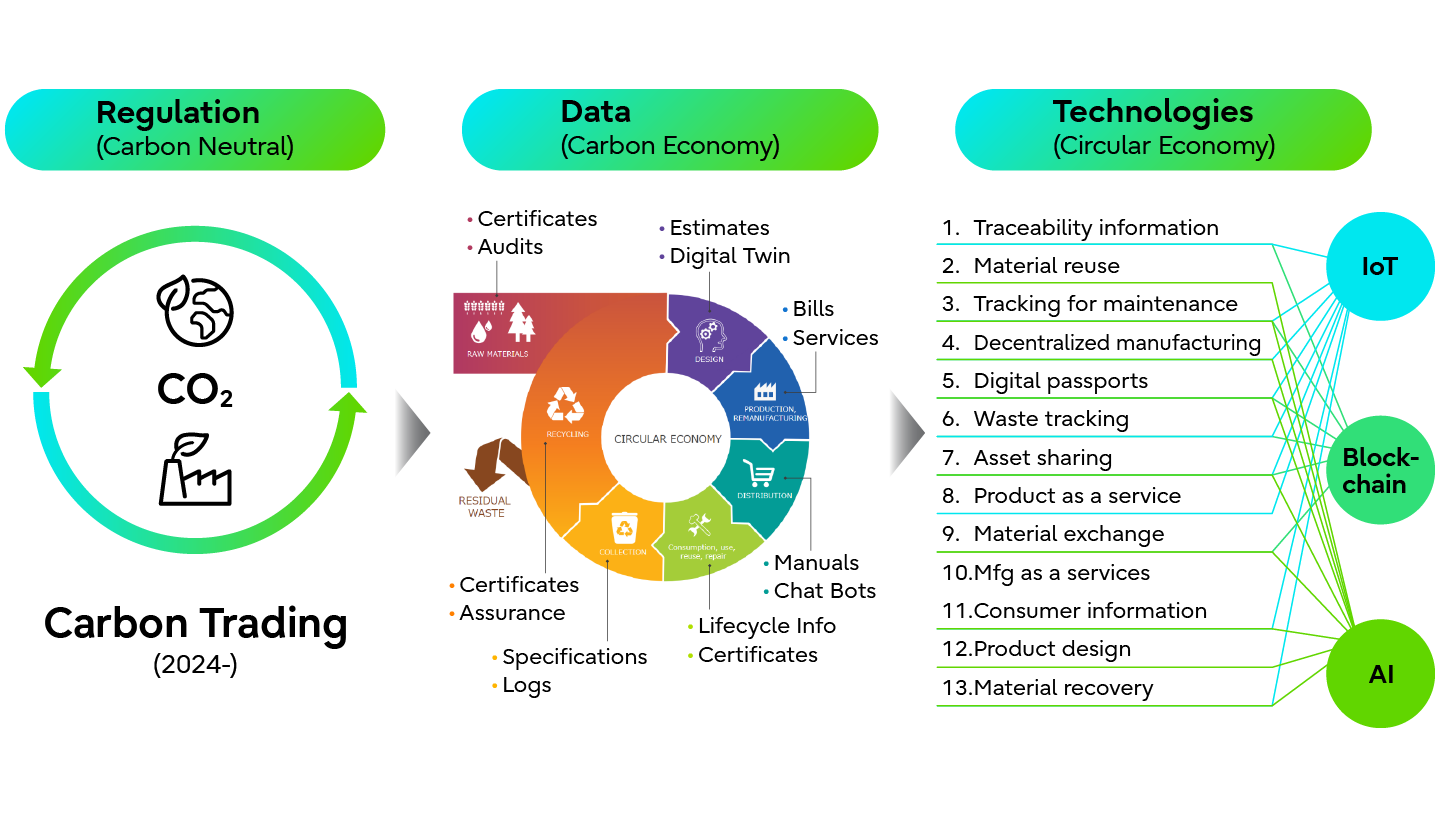
Automotive Industry Leads the Way
The process of AI-based innovation and integration is accelerating as technology and competition begin to transform business models. In the automotive industry, Tesla and Chinese EV companies could gain such a huge advantage by reimagining EVs and their production processes as "software defined" from the ground up. In such cases, sustainable AI strategies offer tremendous opportunities-not only for innovators, but also for incumbents.
As the automotive industry transforms its business model, incumbent internal combustion engine competitors can benefit from effective sustainable AI initiatives, as can their digitally focused rivals. In fact, as their operations become more complex and require even smarter management, incumbents may gain even more. Companies will need to decarbonize their entire supply chains in the best way possible to regain competitiveness. Sustainable AI could help them reimagine their manufacturing operations to identify and manage carbon-intensive components, processes, and suppliers.
By incorporating Sustainable AI into the design and development of their products, manufacturers can take a big step toward an effective Circular Economy with products that use less material, are more durable, and require less maintenance. This not only reduces their environmental impact, but also potentially makes them less expensive to produce, making them more competitive in the marketplace.
Conclusion
Implementing Sustainable AI as part of a business transformation not only offers technological and operational opportunities; by integrating AI into enterprise platforms with sustainability in mind, Sustainable AI becomes a powerful tool for building a more sustainable future. However, developing and implementing Sustainable AI is not a one-time effort. As the World Economic Forum points out, it is a journey towards managing industry in the Intelligent Age.

His work focuses on the impact of digitalization, government policies and corporate strategies. He advises governments and teaches at the Mercator School of Management. His analyses are widely quoted in international media - with regular interviews at CNBC, Bloomberg, NHK World etc. His latest articles include:
Editor's Picks






