Are service and business designers being replaced by AI?
Fujitsu / December 4, 2024
Design was long thought to be "safe" from AI, but that's no longer the case. While AI can't completely replace human interaction, it already excels at many design tasks, performing them quickly and effectively.
The rise of data-driven business
In data-driven business, processes run automatically, and the software manages them, even those conducted by people. Services are optimized based on customer data, and processes adapt automatically to changing customer behaviors. This approach is evident in companies across social media, streaming, taxi services, and food delivery.
However, a crucial element remains: People's economic decisions are heavily influenced by emotions. Are we able to catch the emotional side of things good enough with AI based data driven approach? The answer at least today is that AI-based, data-driven approaches struggle to fully capture this emotional aspect. While AI sentiment analysis tools exist, they currently serve as supplementary tools in service and business design.
Furthermore, data-driven approaches are based on transactions in the past – a rearview mirror perspective. To be successful, businesses must vision the future and build scenarios – projections of the future allowing to make the right business decisions today. The human brain remains invaluable here, though data analysis and AI are powerful supporting tools.
How AI is transforming service and business design
The work of service and business designers is evolving alongside AI. We can analyze this transformation through the lens of the double diamond design process.
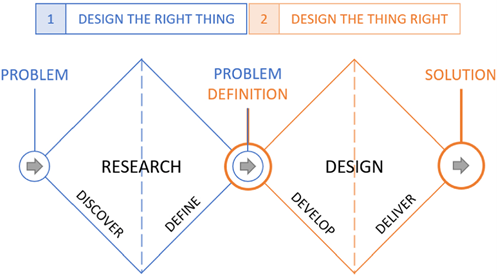
When your business faces challenges during the discovery or research phase, data analytics and various AI solutions can be beneficial. For example, image recognition can supplement live behavioral observation, and generative AI (GenAI) can diversify and speed up the desk research and interview analysis.
Once the problem is clearly defined and the time is right for ideation, AI can be employed. At Fujitsu, we've conducted experiments where we feed GenAI with various insight documents of some business area or company. The GenAI is then able to come up with possible new business ideas for this company. The stakeholders of the company can take these ideas and analyze which of them are worth taking forward.
For testing and prototyping, digital technologies like digital twins and simulation prove useful. These tools allow you to prototype solutions as if they were real. However, this doesn't replace the invaluable feedback of real users, crucial for understanding the emotions and feelings that significantly impact decision-making and service experiences.
Now, let's discuss the challenge of envisioning the future. Data and data analytics are crucial for making predictions. Scenario planning requires extensive desk research, a process that AI can significantly streamline and accelerate.
A case study: Yamagata city's citizen services
Fujitsu's future-creating workshop, incorporating generative AI, exemplifies this transformation. To address the outflow of young people and women from Yamagata City, the “Inspi-talks” were conducted to capture the ideas of young inhabitants. Specifically trained GenAI was then generating short stories envisioning a desirable future for the city. These stories were used as basis in the development of improved citizen services.
The future of service and business design
To conclude I would say that service and business design is adapting to AI, mirroring other business development fields. Customers can anticipate more sophisticated, efficient, and faster design processes, where stakeholders and designers collaborate with AI and digital technologies to enhance business outcomes. The human element, particularly in understanding and responding to emotions, remains a critical component.

Editor's Picks










