Towards a Trusted Society: Using Web 3.0 to facilitate a fairer global economy
Fujitsu / January 11, 2023
The world is constantly changing, and the same can be said for the technology that keeps our society moving. What was once static, controlled, and owned by only a few, now holds the promise of decentralization, flexibility, and real connection. Is it futurology? No, we’re talking about the internet and soon enough, we’ll be talking about “today”.
The birth of the internet has done wonders for society; think Google, Uber or Deliveroo. And it looks like there’s no slowing down as we head towards the next phase in its evolution – Web 3.0.
Emerging technologies such as blockchain and AI have been trending, but not many people understand the impact these technologies will have on the next generation of the internet. From helping us take control and own our data, to creating a more inclusive and equitable world for underprivileged people, Web 3.0 truly has the potential to change the world for good.
In this piece, I explore how Web 3.0 differs from its predecessors and how it stands to disrupt the global power imbalance, by bringing about better equity and inclusion to people around the world.
A brief history
From a static, read-only state – Web 1.0 – the first iteration of the internet had been created by and for a very restricted number of content creators.
The next generation of the internet, Web 2.0, ushered in the era of user-generated content. It was all about the end user's experience and as such, fostered dialogue, collaboration, communities, and eventually, social media. This is the internet as we know it today.
However, this internet is still centralized and governed by a shadow data economy that keeps data in siloes for competitive reasons. As dystopian as it may sound, corporations (the so-called Big Tech) utilize what users produce – valuable data – and sequester them due to its immense possibilities for capitalization.
Web 3.0 however, may be the change we need to see for a future of fairness and transparency. The doors are open to a new era which will see power given back to the user, and by extension, communities all over the world.
It will shift the opaque, shadow approach to data management towards a transparent and permissionless data economy capable of promoting true inclusion. And once a large part of the world’s population data becomes a new and accessible asset class, it will become a tool to achieve a fair economy of resources, money, and information.
Web 3.0 as a differentiator
As blockchain becomes the underlying layer of the web, existing technologies and browsers will still be used. However, blockchain means that trust and transparency will be infused into all activity on the web. Its immutability and decentralized, distributed nature is what allows the data derived from it to be trusted.
In the near future, the internet will evolve from being an extractive economy where you’re the product on centralized platforms such as Google and Twitter, to one where as well as being a consumer, you’re also a provider of services through decentralized, nearly anonymous platforms – a ‘Prosumer’.

Taking back control of your data
In Web 3.0, ownership and control is decentralized. So, unlike with Web 2.0 where content authors were paid often without any real fairness towards the value of their creations – which were all owned by large corporations, Web 3.0 will enable users to own pieces of internet services via tokens that give them ownership rights.
This is where fungible and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) come into play. With the help of these tokens, Web 3.0 will revolutionize our traditional economy and reverse its historic legacy of inequality. Users will be able to pretty much own anything they want in the digital world and receive compensation for its use. From art to music, text, tweets, games, governance rights, and tickets – the list is endless.
More importantly, individuals will be the only owners of their information. As such, they’ll be able to decide what information they want to share and with whom, and even negotiate incentives and terms and conditions for sharing their data with businesses such as marketing firms.
Web 3.0 for underprivileged people
The relationship between consumers, advertisers, and social media platforms will change once the power is given back to people. But how will it become reality? Will Web 3.0 really empower consumers?
Web 3.0 will make a visible, measurable, and verifiable impact on those in society who are facing challenges such as inequality, financial exclusion, and unemployment, as it grants users the ownership of their data, leading to the “creator economy” where brands, corporations, or sponsors will no longer be required.
The rise of SSI (Self-Sovereign Identity) is a clear manifestation of a whole new approach to data management and identity, as it is the application of a completely new model for managing data identities, especially on digital services. If you would like to know more about SSI, its convergence with AI and infinite possibilities, you can check out this blog post.
But how will this new model bring any fairness or change the information network we know, or tip the narrative of power? Here are some ways this will happen:
・Match privileged people looking for investment opportunities with those unable to access funds – creating mutual benefit;
・Build better systems by acting as a catalyst to bring in the right incentives to solve common social problems;
・Open access to lots of different resources that don’t require intermediaries. For example, granting access to digital jobs and the ability to be paid in digital currencies exchangeable to USD or Euros.
The above can be made possible by building first-person relationships using privacy-preserving techniques, such as decentralized security, decentralized connectivity, and decentralized billing.
By applying blockchain technology, Web 3.0 gets back its long-lost goal of decentralization while enhancing the possibilities Web 2.0 brought through apps and interface neutrality. In essence, it could create a democratized era of the internet we’ve never witnessed before.
Facilitating better equity and inclusion for all
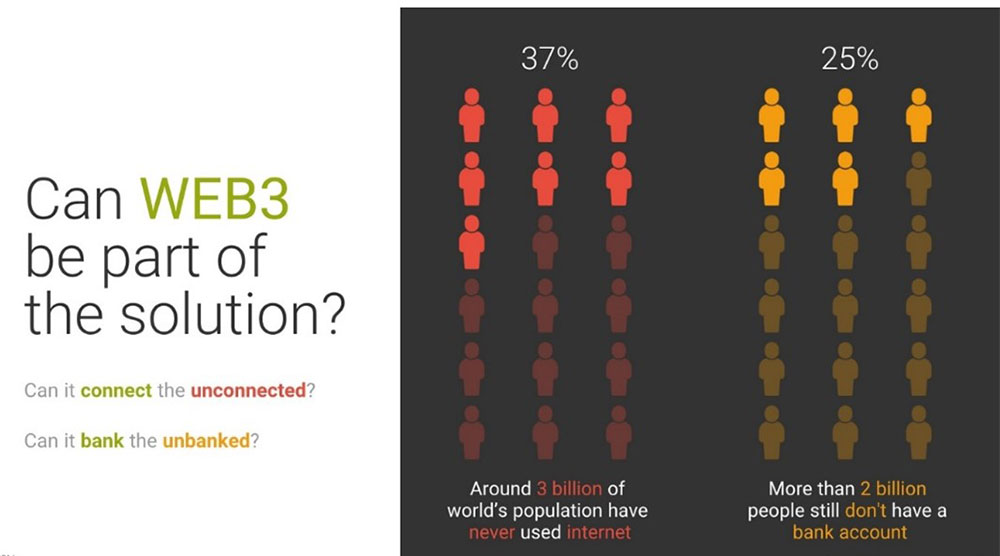
According to Statista, almost 3 billion people have never used the internet, and as such, have been cut off from accessing vital sources of information, communication, and education. How can the reality of these people turn from unconnected to connected?
Web 3.0 can provide the basics of connectivity and bring down infrastructure costs significantly, thereby lowering cost burdens and driving the cost optimization of the network, thus providing a wider opportunity for access.
In small villages in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, South Asia, and Latin America, people are deprived of access to financial services and are deemed ‘unbankable’. More than 2 billion (approximately 25% of the world’s population) are excluded from traditional financial systems. And astonishingly, 70% of them are the farmers that produce one-third of the world’s food supply.
Web 3.0 has the power to change this exclusion from the global economy. Most of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals are rooted in the lack of money flowing into these excluded populations. However, just bringing the money in isn’t enough. For long-term impact, it’s necessary to make sure the change is transformative, so the money keeps coming in even after investors have retrieved their initial investments, by using Web 3.0 technologies to keep track of transactions and ensure ongoing transparency.
Also, low-income forest-dependent communities in Africa or South America will never qualify for carbon sequestration – the list of regulated organizations from which one can buy (offset) traditional carbon credits. That’s because for one to qualify, it must first pay more than $150K for the privilege.
However, with NFTs – which is a fundamental part of Web 3.0 – an individual or organization will be able to hold digital rights to these forests and have associated digital carbon credits (in a voluntary carbon market). This will allow the forest community to monetize their carbon sequestration and in return pay for forest management activities – leading to reinvestment in other forms of livelihood.
Conclusion
We’re in the early adoption stage of Web 3.0 and there’s still some way to go. However, blockchain can create the transparency and real inclusion that global companies and financial superpowers and traditional institutions are unable to provide.
There are still challenges to address in marginalized or excluded global communities, like lack of knowledge and blockchain skills, interoperability between different blockchains, and scalability. These are also some of the challenges hindering the growth of Web 3.0.
However, mainstream adoption will grow as these shortcomings are gradually resolved. And already, great work is being done to improve the scalability and energy efficiency of blockchains, with exciting opportunities to come. This means a real possibility to head towards a more equal world by creating inclusive spaces and tools that promote the eradication of archaic norms such as segregation or hierarchy.
Though there’s still progress to be made, there’s no doubt that when Web 3.0 is truly established, it will change the internet – and our world – as we know it.
Click here to learn more about how you can connect your data and stakeholders in a trusted way for better supply chain transparency and validation.
Make your shift to empowering business and people with digital
Digital Shifts
Fujitsu introduced a key focus area called ‘Digital Shifts’ as a part of its business brand, Fujitsu Uvance.
We enable you and your people to thrive in a fast-changing world and make life more creative.

Related information
Editor's Picks







